Y may be any array. X must be a simple integer scalar or vector. If X is a scalar it is extended to (≢Y)⍴X.
The axis specification is optional. If present, it must be a simple integer scalar or one-element vector. The value of K must be an axis of Y. If absent, the last axis of Y is implied.
R is a vector of items selected from Y by inserting 0 or more dividers, specified by X, between its major cells.
Each element of X specifies the number of dividers to insert before the corresponding major cell of Y. The maximum length of X is 1+≢Y, when the last element of X specifies the number of trailing dividers. Note that major cells of Y that precede the first divider (identified by the first non-zero element of X) are excluded from the result.
The length of R is +/X (after possible extension).
Examples
0 0 1 0 0 1 0⊂'abcdefg'
┌───┬──┐
│cde│fg│
└───┴──┘
2 0 1 3 0 2 0 1⊂'abcdefg'
┌┬──┬─┬┬┬──┬┬──┬┐
││ab│c│││de││fg││
└┴──┴─┴┴┴──┴┴──┴┘
0 2 0 1⊂'abcdefg'
┌┬──┬────┐
││bc│defg│
└┴──┴────┘
The above examples may be explained pictorially by the diagram below.
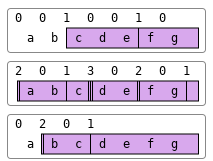
Further Examples
1 0 1⊂[1]3 4⍴⍳12
┌───────┬──────────┐
│1 2 3 4│9 10 11 12│
│5 6 7 8│ │
└───────┴──────────┘
1 0 0 1⊂[2]3 4⍴⍳12
┌───────┬──┐
│1 2 3│ 4│
│5 6 7│ 8│
│9 10 11│12│
└───────┴──┘